The Founding of Gucci
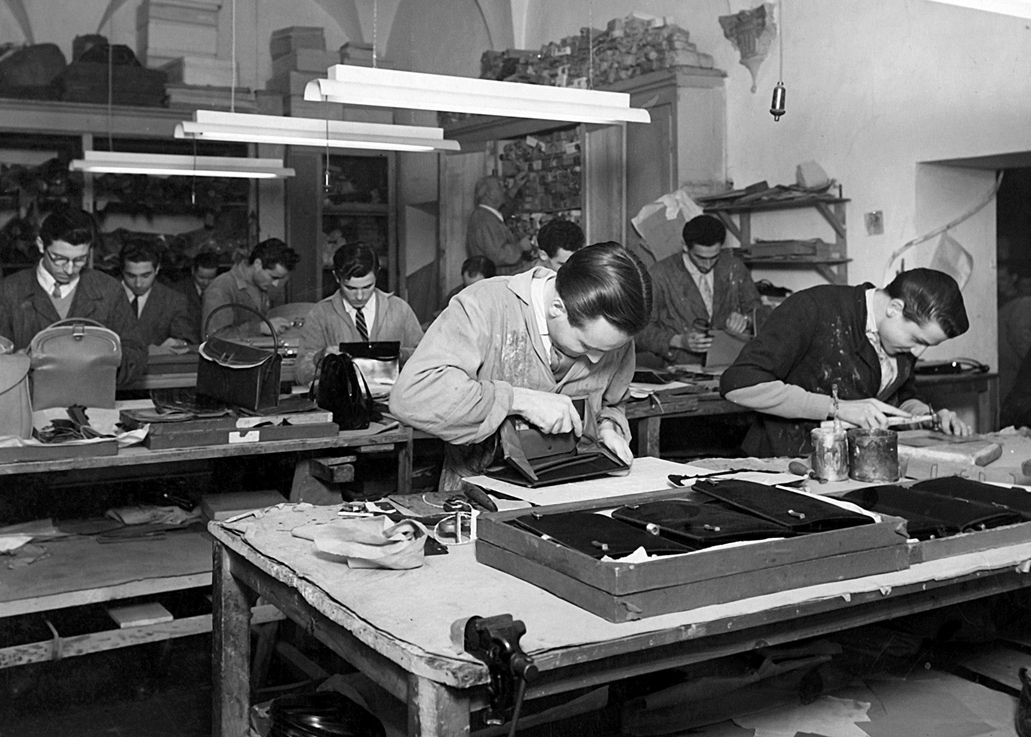
At the beginning of the 19th century, the Gucci company became one of the world’s most successful manufacturers of high-end leather goods, clothing, and other fashion products. As an immigrant hotel worker in Paris and later London, young Guccio Gucci (1881–1953) was impressed with the luxurious luggage he saw urbane guests bring with them at the Savoy Hotel. Before leaving, he visited the manufacturer, H.J. Cave & Sons. Upon returning to his birthplace of Florence, a city distinguished for high-quality materials and skilled artisans, he established a shop in 1920 that sold fine leather goods with classic styling. Although Gucci organized his workrooms for industrial methods of production, he maintained traditional aspects of fabrication. Initially, Gucci employed skilled workers in basic Florentine leather crafts, attentive to finishing. With expansion, machine stitching was a production method that supported construction.